This section describes different types of evaluation designs and outlines advantages and disadvantages of each. Many alternative designs can also be created by adding a comparison group, follow-up test, retrospective pretest, and/or intermediate testing to the designs identified below.
Posttest only
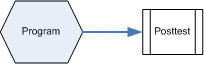
Data are collected at the end of the program.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| This type of evaluation design is useful when time is an issue or participants are not available before the program begins | Because there is no pretest or comparison group, it is difficult to determine:
|
Retrospective Pre & Posttest
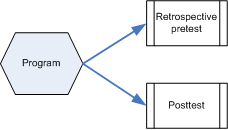
Data are collected at the end of the program. Participants are asked to assess their current level of knowledge/attitudes/skills/intentions AFTER experiencing the program and to reflect on their previous level of knowledge/attitudes/skills/intentions BEFORE experiencing the program.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Useful when a true pretest is impossible | Some may find it difficult to remember how they thought/behaved prior to the program |
Pre & Posttest
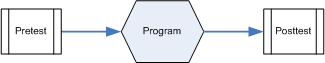
The same instrument is used to collect data before the program begins and again at the end of the program.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
Pre & Posttest with Comparison Group
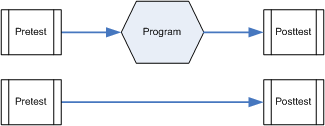
Data are collected before the program from two groups. One group participates in the program and the other does not. Data are collected from both groups once the program has ended.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
Pre & Posttest with Follow-Up
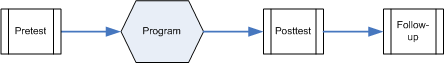
Data are collected before the program begins, at the end of the program, and again at some point in the future.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|
|
Intermediate Testing & Posttest
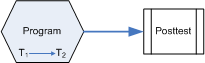
Data are collected at multiple points during the program (T1 and T2 in diagram) and again at the end of the program.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Allows you to track participants’ progress as they move through the program |
|
Note: Use of these designs is not limited to quantitative methods. Qualitative methods can also be used with these designs.
References
Adapted from Bennett, D.B. (1984). Evaluating Environmental Education in Schools: A practical guide for teachers. Retrieved July 26, 2006 from http://unesdoc.unesco.org/images/0006/000661/066120eo.pdf
